Author: Luis Flavio Nunes
Compiled by: Deep Tide TechFlow
Deep Tide Introduction: On January 29, 2026, Bitcoin plummeted 15% in a single day, falling from $96,000 to $80,000. The strangeness lies in this: when the stock market crashed, it should have risen as a safe-haven asset, but it fell; when the Federal Reserve signaled a hawkish stance, it should have fallen as a risk asset, but it also fell. Bitcoin collapsed in both opposing events.
This article points out that Bitcoin is simultaneously playing four contradictory identities: inflation hedge, tech stock, digital gold, and institutional reserve asset. When these four identities vie for control, the result is chaos.
The author proposes four possible resolution paths and analyzes which path will push Bitcoin to $150,000.
Full text as follows:
On January 29, 2026, Bitcoin plummeted 15% in a single day, falling from $96,000 to $80,000. What is striking is not the crash itself, but that Bitcoin fell during two simultaneous, opposing events.
The stock market crashed. This should have helped Bitcoin as a safe-haven asset.
The Federal Reserve signaled tightening policy. This should have hit Bitcoin as a risk asset.
Bitcoin collapsed in both events. It moved with stocks when it should have moved opposite them. It fell on hawkish news when digital gold should have risen. The fundamental logic of the market's understanding of what Bitcoin actually is was broken.
Four Incompatible Identities
Bitcoin is simultaneously traded as four different assets. Each identity demands different price behavior. When all four identities vie for control, the result is chaos.
Identity One: Inflation Hedge
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins. When governments print money and devalue currency, Bitcoin should rise. This was the original promise. Digital scarcity triumphs over government printing presses.
The data tells a different story. In 2025, when inflation fears dominated the markets, gold rose 64%. Bitcoin fell 26%. When the Consumer Price Index (CPI) showed unexpected increases, Bitcoin sometimes rose. When Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (Core PCE) showed inflation, Bitcoin sometimes fell. The reaction was random, not consistent.
If Bitcoin were truly an inflation hedge, it should react the same way to all inflation signals. Instead, it reacts to some signals and ignores others. This suggests Bitcoin is reacting to something else, perhaps energy prices that affect mining costs and consumer inflation.
Identity Two: Tech Stock
Bitcoin moves in sync with the Nasdaq. The 30-day correlation reached 0.68. When tech stocks fall on growth concerns, Bitcoin falls. When the Fed hints at tightening and tech stocks sell off, Bitcoin sells off harder.
If Bitcoin is a tech stock, investors might as well buy the Nasdaq index directly. Tech stocks don't pay dividends, but they generate revenue and profits. Bitcoin generates neither. A pure tech bet through actual tech stocks makes more sense.
The problem goes deeper. Bitcoin was supposed to be uncorrelated with traditional markets. That was the whole value proposition. If Bitcoin is just a leveraged Nasdaq bet, it has no place in a portfolio already holding stocks.
Identity Three: Digital Gold
In late January, when investors fled risk, gold soared to $5,500. Bitcoin crashed to $80,000. At the exact moment digital gold should have proven its value, the two assets moved in opposite directions.
Bitcoin's correlation with gold turned negative in 2026. Precisely negative 0.27. When gold rose 3.5% on hawkish Fed news, Bitcoin fell 15%. The Bitcoin-to-gold ratio hit a record low of 16.68x.
If Bitcoin is digital gold, it failed the most basic test. Gold works as a crisis hedge because it moves away from risk assets when panic rises. Bitcoin moves with risk assets, proving it is not gold in any meaningful sense.
Identity Four: Institutional Reserve Asset
Some companies and governments hold Bitcoin as a strategic reserve. Japan's Metaplanet holds 35,100 Bitcoin. The US government integrates seized Bitcoin into its strategic reserves. This narrative suggests Bitcoin will become a core holding for pension funds and central banks.
The behavior doesn't match the story. Institutional investors are not holding through volatility. They are running basis trades, selling volatility, and treating Bitcoin as a trading tool. ETF flows mainly show arbitrage activity, not long-term conviction buying.
If institutions truly saw Bitcoin as a reserve asset like gold, they would accumulate during crashes and never sell. Instead, they sell during crashes and buy on rallies. This is trader behavior, not reserve manager behavior.
Valuation Paradox
Each identity implies a different fair value for Bitcoin.
If Bitcoin is an inflation hedge, based on gold's performance under similar monetary conditions, the price should be $120,000 to $150,000.
If Bitcoin is a tech stock, based on correlation with the Nasdaq and lack of cash flow, the price should be $50,000 to $70,000.
If Bitcoin is digital gold, based on gold's 65-year value trajectory applied to digital scarcity, the price should exceed $150,000.
If Bitcoin is an institutional reserve asset, the price should track government and corporate adoption rates, suggesting a year-end level of $100,000 to $120,000.
The current price of $80,000 satisfies none of these frameworks. It is in the middle, pleasing no model and validating no thesis. This isn't the market finding equilibrium. It's a market that cannot agree on what it is pricing.
When Wall Street Can't Define What It Owns
Robbie Mitchnick manages digital asset strategy at BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager. In March 2025, he said something remarkable:
"Bitcoin fundamentally looks like digital gold. But some days it doesn't trade like that. Tariffs get announced, and it falls like a stock, which confuses me because I don't understand why tariffs would affect Bitcoin. The answer is they don't."
Even Bitcoin's primary institutional advocates admit confusion. If BlackRock doesn't understand what Bitcoin is, how can retail investors be expected to know?
This confusion creates a mechanical problem. When institutions cannot classify an asset, they default to correlation-based risk models. These models assume historical correlations persist. When correlations shift suddenly, as in January, institutions must rebalance their portfolios. Rebalancing during a crash means forced selling. Forced selling creates a cascade effect.
Think of it like a ship's autopilot. The autopilot steers based on past wind patterns. When the wind suddenly changes direction, the autopilot overcorrects, causing violent swings. Human judgment could smooth the course, but the autopilot only knows historical patterns. Bitcoin's identity crisis is the changing wind, and the institutional algorithms are the autopilot overcorrecting in the storm.
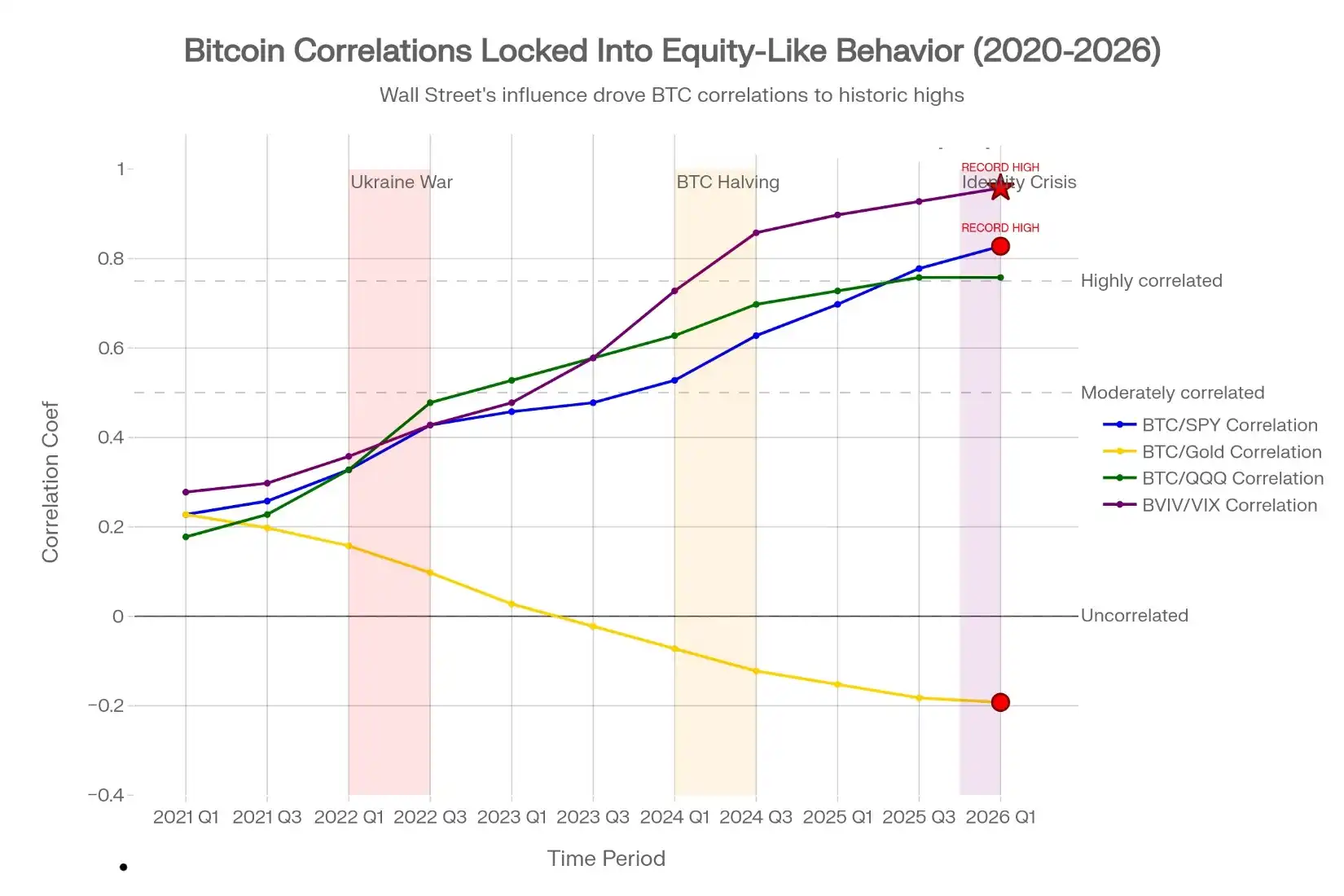
The Death of Diversification: Bitcoin's correlation with stocks surged from 0.15 (2021) to 0.75 (January 2026), a five-year shift driven entirely by institutional risk management, not Bitcoin adoption or fundamentals. The more damaging metric: Bitcoin volatility now correlates with stock volatility at 0.88 (purple line), the highest level ever recorded. This proves Bitcoin is traded mechanically based on stocks, not its own utility. Investors buying Bitcoin as a hedge are actually buying a leveraged, volatile stock bet, amplifying losses during crashes rather than offsetting them.
Volatility Homogenization
Bitcoin's volatility now moves in sync with stock market volatility. The correlation between Bitcoin volatility and the VIX stock volatility index reached 0.88 in January 2026. This is the highest reading ever recorded.
In 2020, this correlation was 0.2. Bitcoin volatility was independent. By 2026, it had become identical to stock volatility.
This is because institutional traders sell volatility across all asset classes simultaneously. When the VIX rises above certain levels, algorithms automatically sell Bitcoin, stocks, and commodities to reduce portfolio volatility. This mechanical selling has nothing to do with Bitcoin fundamentals. It is pure risk management, applied equally across all assets.
The result is that Bitcoin has lost independent price discovery. Its price is no longer driven by adoption, usage, or scarcity. It is driven by correlation assumptions and volatility control algorithms.
The data proves this. In January 2026, even as the price rebounded to $96,000, Bitcoin's daily active addresses were declining. Transaction volume was falling even as institutional adoption was supposedly accelerating. The Lightning Network, which processes actual Bitcoin payments, grew 266% year-over-year. Yet the price fell.
Usage was up. Price was down. This proves that what drives the price is positioning and correlation, not fundamentals.
Reflexivity Trap
George Soros described reflexivity as a feedback loop where price movements themselves drive further movements, independent of fundamentals.
Bitcoin is caught in reflexivity.
Institutions assume a 0.75 correlation between Bitcoin and stocks. Options traders build hedges based on this assumption. When stocks move 2%, algorithms trigger a 2% move in Bitcoin. This creates a self-fulfilling prophecy. Bitcoin moves with stocks, so traders think it's a stock. Retail investors adopt this view and trade accordingly. The actual Bitcoin fundamentals become irrelevant. The price is completely detached from utility.
This is not temporary confusion. It is structural. Until institutions agree on what Bitcoin is, the reflexivity loop will persist. Every rally will contain the seeds of the next crash because the market cannot agree on why the rally is happening.
What Retail Investors Actually Own
Most retail investors think they are buying diversification when they buy Bitcoin. They believe Bitcoin protects against inflation and reduces stock exposure. The math proves otherwise.
Take a simple example. An investor holds $100,000 in stocks and allocates $5,000 to Bitcoin, expecting diversification.
When stocks fall 10%, the portfolio loses $9,000. But Bitcoin, with a 0.75 correlation to stocks, falls 15%. The Bitcoin position loses $750. Total loss: $9,750.
Without Bitcoin, the loss would have been $9,000. Bitcoin made the portfolio worse, not better. This correlation means Bitcoin amplifies stock losses, not offsets them.
True diversification requires negative correlation. Bonds are negatively correlated with stocks during risk-off periods. Gold is negatively correlated during crises. Bitcoin is positively correlated, making it useless as a hedge.
The Inevitable Resolution
Bitcoin cannot sustain four conflicting identities. The market will force a resolution in 2026 through one of four paths.
Path One: Strategic Reserve
Governments and corporations treat Bitcoin like gold reserves. They buy and never sell. Price volatility becomes irrelevant as holders measure success in decades, not quarters. Institutions stop trading Bitcoin and start hoarding it. Price finds equilibrium based on slow, steady accumulation. This path leads to $120,000 to $150,000 by year-end.
Path Two: Risk Asset Normalization
Institutions formally classify Bitcoin as a commodity derivative or stock analogue. They build risk models that account for extreme volatility. They accept that Bitcoin is not a hedge but a leveraged bet on monetary expansion. Position sizes are adjusted accordingly. Correlations become predictable because everyone agrees on what Bitcoin is. Price trades in an $80,000 to $110,000 range with lower volatility.
Path Three: Inflation Hedge Acceptance
After resolving which inflation metric matters, the market agrees Bitcoin reacts to monetary debasement, not consumer price changes. Correlation with stocks falls to 0.3 or 0.4. Bitcoin becomes a true alternative to gold. This path leads to $110,000 to $140,000 as portfolio managers allocate for inflation protection.
Path Four: Diversification Failure
Institutions realize Bitcoin cannot diversify a stock portfolio. A 0.75 correlation is too high to justify an allocation. Capital flows reverse as portfolio managers exit. Retail investors understand Bitcoin is not a hedge. Price falls to $40,000 to $60,000 as the strategic allocation story collapses.
The most likely outcome is a slow resolution in 2026. Bitcoin will gradually shift from risk asset to reserve asset, with periodic corrections as institutions recalibrate. Price will consolidate between $80,000 and $110,000 until one path dominates.
What to Watch
Four indicators will show which path Bitcoin takes.
- Correlation Inflection: If Bitcoin stops moving with stocks and correlation drops below 0.5, it becomes a hedge again. This favors Path Three.
- Government Announcements: If a major government formally allocates Bitcoin to reserves, Path One accelerates. Watch for announcements from the US, EU, or Japan.
- On-Chain Metrics: If daily active addresses and transaction volume reverse higher while price is flat or falling, fundamentals are improving even as speculation wanes. This suggests long-term strength.
- Volatility Normalization: If the correlation between Bitcoin volatility and stock volatility drops below 0.60, institutional volatility selling is easing. This allows true price discovery to return.
These indicators don't require capital to track. They provide better insight than price charts.
Conclusion
Bitcoin's fall to $80,000 was no accident. It was Bitcoin confronting a question it has avoided since institutional money arrived: What am I?
Until this question has a clear answer, every rally will contain the seeds of the next crash. Bitcoin will move with stocks when it should diverge. It will fall on news that should help it. It will rise on developments that shouldn't matter.
This is not temporary confusion. It is a structural identity crisis that will define the entire 2026 narrative.
Investors buying Bitcoin as an inflation hedge will be disappointed during inflation panics. Investors buying it for diversification will be disappointed when it amplifies stock losses. Investors buying it as digital gold will be disappointed when it trades like a tech stock.
The only investors who will succeed are those who understand that Bitcoin is currently none of these things. It is a positioning-driven, correlation-dependent, volatility-controlled instrument that has temporarily lost its connection to its fundamental purpose.
The crash exposed this truth. The recovery will depend on Bitcoin's ability to answer what it is before the institutions decide the answer for it.